Fan Regulator; Function of fan regulator ; Why Fan regulator required
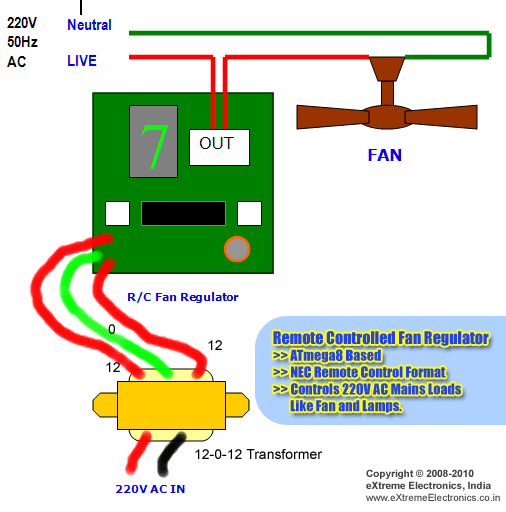
A fan regulator is an important element that functions to raise or reduce the rate of your fan according to your own demands. You've got a choice between electronic and traditional regulators. Regulators Standards Older variants of traditional regulators were rather bulky to examine. A square carton jutting from a plank with a ring-shaped toggle or knob switch failed to make for quite glossy look. The box included the circuit components of the regulator system. You'd to fix the knob to place the fan at the desired rate. Modern day only a toggle is presented by standard regulators on a panel that includes the switches for the other electrical devices. You may not really get to see the modulating unit hidden in the wall behind the plank. You must know something to comprehend how a regulator functions. The conductor nevertheless, offers a specific amount of opposition to the passage of current. The resistance is determined by the substance of the conductor. The regulator has spool
.jpg)